Prisijungti / Registruotis
Prisijunkite arba registruokitės
Prisijungti Sukurti paskyrą- Filtration
- Final Filling
- Flexact® Modular | Single-use Automated Solutions
- Inoculation Preparation
- Freeze & Thaw
- Liquid Storage & Shipping
- Mixing
- Sterility Testing
- Process Chromatography
- Transferring & Sampling
- ABLE Bioreactors
- Ice buckets
- Ice free temperature holders
- Cell freezing systems
- Cryo Bio System™ straws, tubes and accessories
- Cryo vials and accessories
- Autoclavable Bags
- Blender Bags
- Bottles
- Inoculation loops
- Membrane Filters
- Microscope slides
- Petri dishes
- Spatulas
- 3D cell culture
- Erlenmeyer flasks and caps
- TC flasks
- TC plates
- TC dishes
- Bottles
- Cell scraper, cell lifter
- Serological pipettes
- Prefiltration (Sartoguard, Sartoclean®, Sartopure®)
- Filter Holders and Housings
- Filtration of Cell Culture Media (Sartopore®, Virosart®)
- Cell Harvesting (Sartoclear®) Depth Filters
- Sterile Filtration (SartoScale 25, Sartopore® Platinum, Sartopore® 2, Sartobran®, Sartolon, Maxicaps®)
- Tangential Flow Filtration
- Virus Filtration (Virosart®)
- Air, Gas Filtration (Sartopore® Air, Midisart®, Sartofluor®, Sartopure® GA)
- Aseptic Bottle Closure MyCap
- Erlenmeyer flasks and caps
- Microcarriers
- Roller bottles
- Spinner flasks and closures
- Stackable cell culture
- Storage bottles
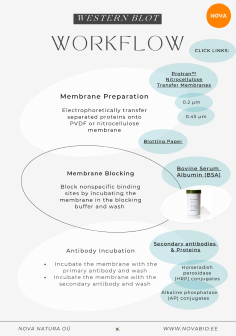
- Blotting
- Filter Papers
- Filtration Equipment
- Glass & Quartz Microfibre
- Quartz Microfiber Filters
- Membrane Filters
- Polycarbonate Track-Etched Membrane Filters
- Syringe Filters
- Capsules (Scale Down Devices)
- Chromatography Spin Columns
- Lab Units (Not Scalable)
- Sartobind® 96-well plates
- Automated nucleic acid extraction kits
- Immunological rapid tests
- Real-time PCR reagents for diagnostics
- Cell culture surface coatings, extracellular matrices
- Cell culture growth factors, cytokines, additives
- Cell culture media, buffers, serum
- Cytogenetics Reagents
- Cell culture buffers
- Cell culture media
- Cell culture reagents
- Cell culture grade water
- Cell culture serum
- Fluorescent Probes for Organelles & Subcellular Compartments
- Fluorescent Secondary Antibodies
- Cell Painting Kits
- Bioluminescent Bacteria
- Bioluminescent Substrates and Lentiviral Particles
- Bioluminescent Oncology Cell Lines
- Fluorescent Nanoparticles
- Fluorescent Imaging Panels
- Fluorescent Agents
- Fluorescent Labeling Kits & Dyes
- Radioimaging & Radiotherapeutics
- Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA)
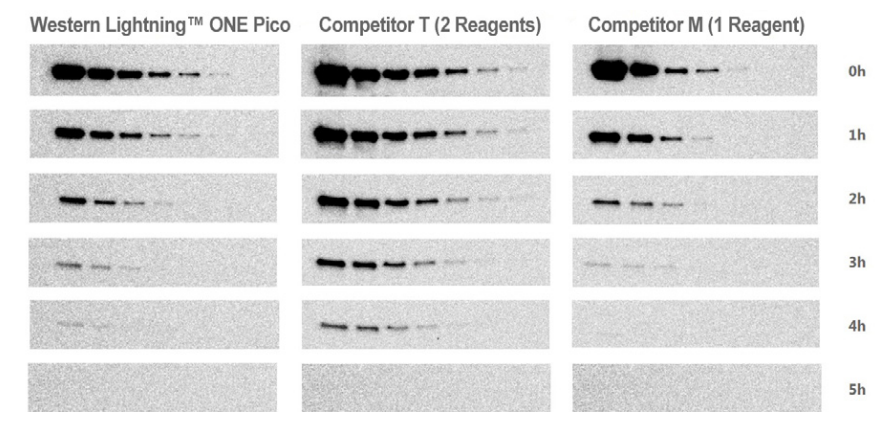
- Chemiluminescent Blotting Substrates
- Chromogenic Substrates
- Secondary Antibodies & Proteins
- Bioreactors & Fermenters
- Filtration
- Freeze & Thaw
- Palletank
- Cell Harvesting
- Mixing
- Sterility Testing
- Integrity Testing
- Connecting & Disconnecting
- Weighing Accessories
- Laboratory Balances
- Mass Comparators & Metrology
- Moisture Analyzers
- Paint Mixing Solutions
- Gel documentation system
- Cell Lysis
- Constant Temperature Equipment
- Shakers & Mixers
- Stirrers and Stirring Hot Plates
- Plate Sealer
- Cell counter
- Thermal Cycler
- Centrifuge
- Water Purification
- Osmometers
- NEW IVIS Lumina S5 & X5
- IVIS Lumina III Series
- IVIS Spectrum Series
- Quantum GX2 microCT Imaging System
- Rotating Angle Dynamic Light Scattering (RADLS)
- UV/Vis Spectroscopy
- Differential Scanning Fluorimetry (DSF)
- Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
- Static Light Scattering (SLS)
- Microfluidic Mixing
- Single Particle Interferometry
- Microfluidic Viscosity Measurements
- Ultrafiltration & Diafiltration (UF/DF)